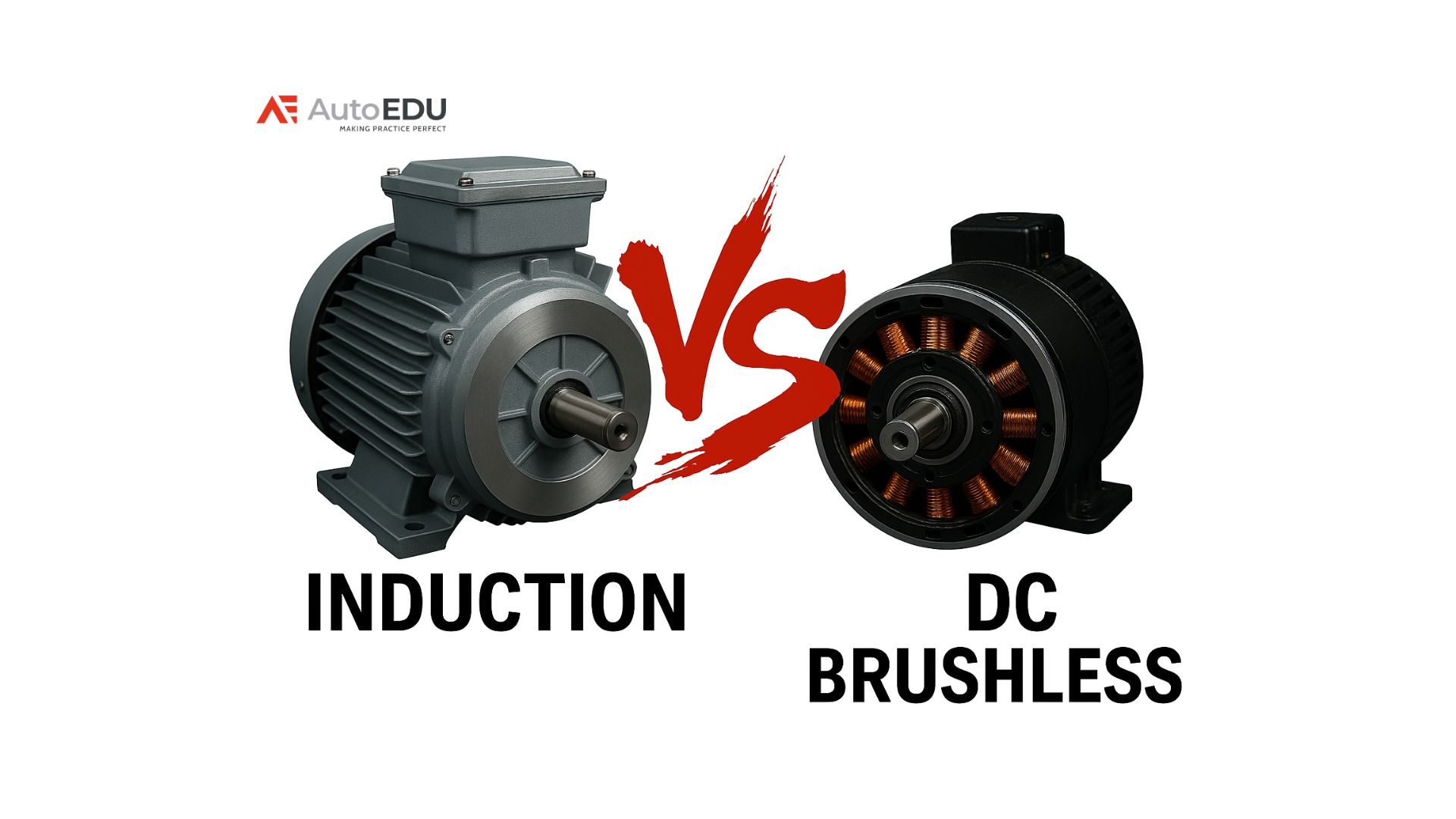
Electric motors are everywhere in modern vehicles, powering everything from main drive systems to small accessories. The two most common types in automotive use are induction motors and DC brushless (BLDC) motors. Both convert electrical energy into mechanical movement, but their designs and performance are different. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone working with automotive technology or pursuing technical training.
Induction Motors: Principles and Applications
Induction motors, also known as asynchronous motors, are valued for their simplicity and reliability. Their main parts are the stator, which holds the wire windings, and the rotor, which is made of steel laminations and conductive bars.
When AC power flows through the stator, it creates a rotating magnetic field. This field induces current in the rotor without any physical electrical connection. The interaction between the induced rotor current and the stator’s magnetic field produces torque, which turns the rotor.
Induction motors are highly durable and need little maintenance since they have no brushes or commutators. Their speed depends on the AC supply frequency and the motor’s design. In automotive systems, induction motors are common in electric vehicle traction drives, HVAC blowers, and various electric pumps. They are chosen where simple, robust, and reliable power is needed.
DC Brushless Motors (BLDC): Principles and Applications
DC brushless motors work differently. They use a permanent magnet rotor and an electronically controlled stator. Sensors, usually Hall-effect, monitor the rotor position so the controller can switch current to the correct stator windings. This electronic commutation leads to high efficiency and very precise speed and torque control.
Because there are no brushes, BLDC motors require minimal maintenance and are quiet with low vibration. They are widely used in electric power steering, cooling fans, electric window lifters, and many electronic accessories in modern vehicles. BLDC motors are ideal where precise, efficient, and reliable control is required, even in compact spaces.
Where These Motors Are Most Commonly Used
Induction Motors:
-
Main electric drive systems in electric vehicles (EVs), especially in larger or older EV models.
-
Industrial automotive equipment such as lifts, compressors, and heavy-duty pumps.
-
HVAC blowers and coolant pumps in commercial and specialty vehicles.
DC Brushless Motors (BLDC):
-
Electric power steering systems, due to the need for responsive and smooth control.
-
Cooling fans for engines and batteries, which benefit from variable speed operation.
-
Electric windows, seat adjusters, and sunroof drives.
-
Hybrid and newer electric vehicle propulsion systems, where high efficiency and compact design are critical.
Why It Is Important to Understand the Differences
Understanding the differences between induction and BLDC motors is crucial for several reasons:
-
Correct Motor Selection: Each motor type is suited for specific automotive tasks. Using the wrong motor can lead to inefficiency, higher costs, or mechanical failure.
-
Effective Troubleshooting: Diagnosis and repair procedures differ between motor types. Knowing how each operates ensures accurate and efficient maintenance.
-
Advancing Technology: Automotive technology is evolving rapidly. New vehicles increasingly use BLDC motors for advanced features, while some systems still rely on the robustness of induction motors.
-
Training and Safety: Handling and servicing electric motors requires technical knowledge. Awareness of motor types and their control systems is essential for safety and professional development.